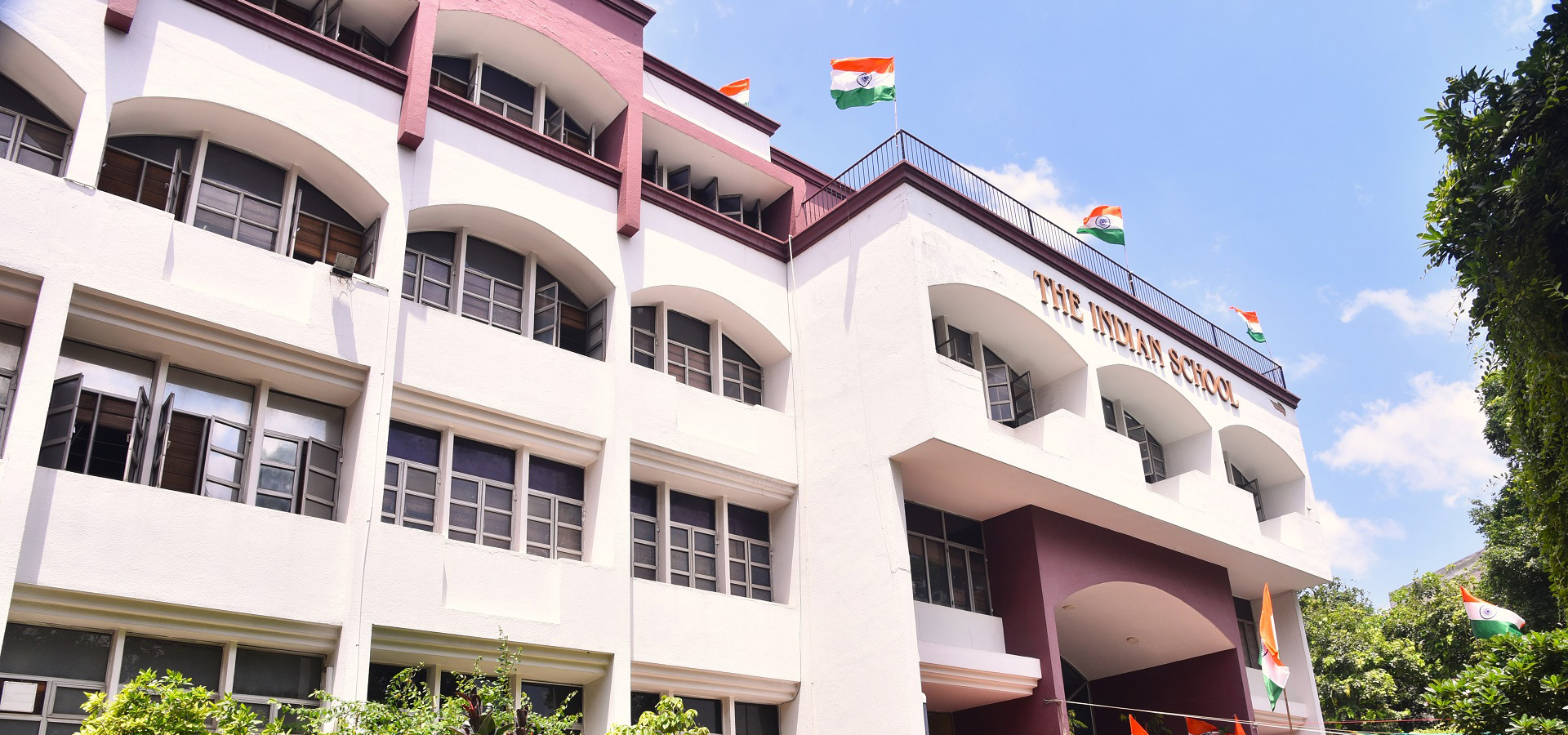
Visit To The National Physics Laboratory
On 27th September 2016, 30 students from classes 10, 11 and 12 had the opportunity to visit NPL ( the National Physics Laboratory). They were accompanied by their teachers, Ms. Archana Raichandani, Mr. Pallab Roy and Dr. Smriti Singh. The event was organised by the CSIR Foundation.
CSIR-NPL is one of Indias top science and research laboratories. It is also one of the world's leading centres in developing and applying the most accurate standards of length, mass, time, voltage, current and force. Its facilities are amongst Indias most extensive and sophisticated for the measurement of quantum physics, materials and materials& characterisation, nanoscience and nanotechnology, energy harvesting, surface science, thin films, radio and atmosphere sciences, environmental sciences, superconductivity and low temperature physics.
Our students were taken around the various sections of NPL to get a clear idea of the kind of work they are doing.
LENGTH, DIMENSIONS AND VOLUME MEASUREMENT SECTION
In this section of the lab, students found out how the accurate measurement of machine parts takes place. A system of coordinates is used to measure the length of different parts. This coordinate system is then calibrated with the machine. The part to be measured is kept on the surface of a machine and the coordinates of this part are taken. These l coordinates are then matched with the ideal coordinates of that machine part and a comparison is made. If there are variations, these are named in the certificate issued by NPL.
[gallery link="file"]
LIQUID HELIUM PLANT SECTION
In this section of NPL, students were shown the liquefaction of helium (which is only 0.05%in the atmosphere). There were two big tanks, one was a distillation tank in which helium is extracted from a mixture of gases and transported through a coil of pipes into a cooling tank or condenser. The temperature of helium is lowered here and is then transported to another tank (compression tank) where the cool helium gas is liquefied. It is then stored in cylinders and transported for industrial purposes.
CRYSTAL GROWTH AND ITS USES
In this section of NPL, students were shown how crystals of different elements or compounds such as NaCl, silicon, copper sulphate and arsenic are formed. These crystals are formed by using big tanks which have heating and condensing facilities. These large crystals cannot be put to use directly so, for utilisation purposes these crystals are converted into wafers or very thin pieces. These wafers are found in electronic chips or in solar cells.
NPL AUDITORIUM
Finally, students went to the NPL auditorium and were shown a film about the extraordinary working of the different sections of the NPL. Later, an interesting activity of slogans took place in front of the main building, where we were asked to shout out aloud the names of some famous science researchers. The technicians then measured the intensity of the sound produced in decibels for the different groups.
The visit to NPL was an unusual experience for our students. They were shown an interesting range of instruments and procedures at the laboratory that were both eye-opening and extremely informative.
Dr. Smriti Singh.